Mars is the 2nd smallest planet in the solar system next to Mercury. It’s also the 4th planet from the sun, and the second closest planet to Earth.
Mars is approximately half the size of Earth (which is the solar system’s 4th smallest planet) in terms of diameter, 53% to be exact. Of course, when you’re trying to answer the question “how big is mars”, there are a number of ways to arrive at an answer, depending on the measurements you want to look at.

Comparison of Earth and Mars (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
Diameter & Circumference
Although it looks round, Mars isn’t a perfect sphere. Like Earth, Mars bulges at the equator, giving it a diameter of 4,222 miles (6,794 km) at the equator but 4,196 miles (6,752 km) when measured from pole to pole.
This of course also means that the circumference of mars measured around the equator (13,300 miles, 21,343 km) is longer than the circumference measured around the poles (13,200 miles, 21,244 km).
Mass & Surface Gravity
At 6.42 x 1023 Mar’s mass is about 10% of Earth’s. Because of its smaller mass and smaller diameter, the gravitational pull on Mars is only 38% of Earth’s. If for example you weighed 100 lbs on Earth, you would only weigh 38 lbs on the surface of Mars.
Highest Peak & Deepest Valley
Mars is a planet of extremes. This desert planet is home to both the highest peak as well as the deepest valley in the solar system.
The highest peak on Mars is Olympus Mons, a large shield volcano. It has a height of almost 14 miles (22 km), making it 3 times taller than the tallest mountain on earth, Mt. Everest. not only the tallest mountain in the entire solar system, but the 2nd tallest mountain of any known planet in the universe.
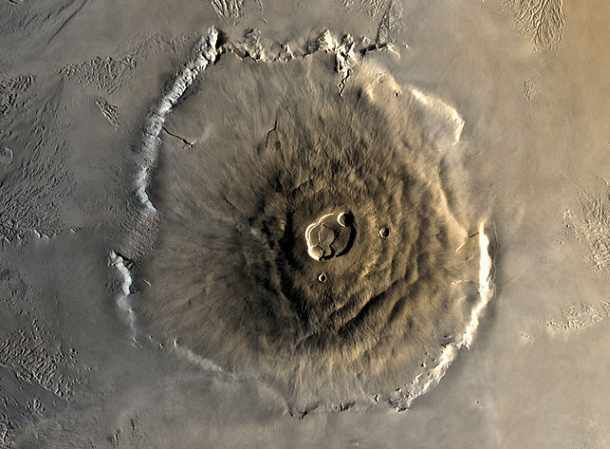
Olympus Mons (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
Although Olympus Mons is 3 times the size of Everest, if you were standing at its top, you wouldn’t realize you were standing on a massive mountain. Because of the vastness of the volcano, its extremely gentle slope, and the short horizon on Mars (3km) you would only see that you were standing on a gently rising hill.
By the same token, an observer standing on the martian surface wouldn’t be able to see the full profile of this vast mountain, no matter how far they stood.
The deepest valley on Mars is also the deepest and longest valley in the entire solar system. Valles Marineris is 1,800 miles (3,000 km) long. From space, it looks like a giant gash on the martian surface. The walls of the canyon dive 28,000 feet (8,500 meters) to the valley floor - that’s almost the height of Mount Everest here on earth. That’s also nearly 5 times the depth of the Grand Canyon.
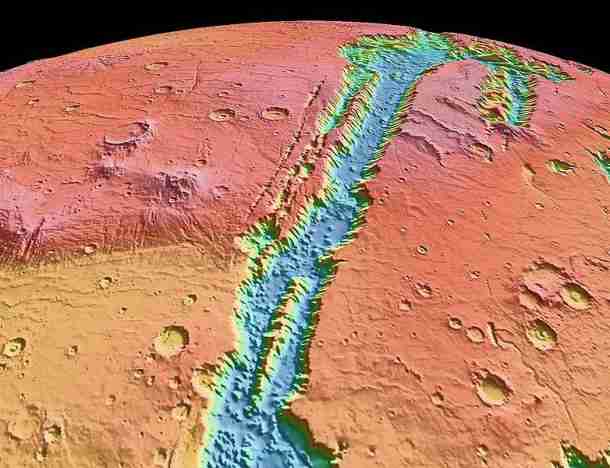

Valles Marineris topographic view constructed from MOLA altimetry data. (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
Orbit
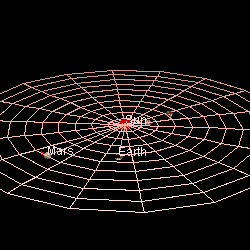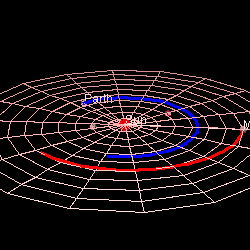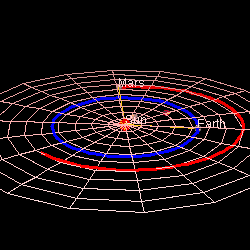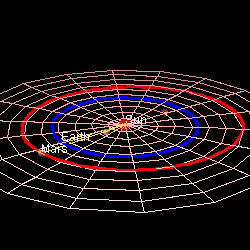
Mars' Orbit In Comparison To Earth's (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
However, a Martian day is only slightly longer than that of Earth, at 24 hours and 39.5 minutes.
Mars is approximately 230 million miles (369 million km) away from the Sun. By comparison, Earth is 93 million miles (149 million km) away from the sun.
Because Mars has a tilt in its axis just like Earth it also experiences seasons, though Martian seasons are around twice as long as Earth seasons due to the longer year.